| Entry |
|
|---|
| Name |
Teichoic acid biosynthesis |
|---|
| Description |
Teichoic acids (TAs) are a class of cell surface glycopolymers found in the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria. They are anionic polymers consisting of glycerol phosphate (GroP) or ribitol phosphate (RboP) repeat units linked by phosphodiester bonds. There are two types of teichoic acids: wall teichoic acid (WTA), which is attached to peptidoglycan by a disaccharide linkage unit, and lipoteichoic acid (LTA), which is attached to the plasma membrane by the Glc-DAG anchor. The repat units of both WTA and LTA may further be modified by glycosyl residues and/or D-alanine esters, generating structural variations.
|
|---|
| Class |
Metabolism; Glycan biosynthesis and metabolism
|
|---|
| Pathway map |
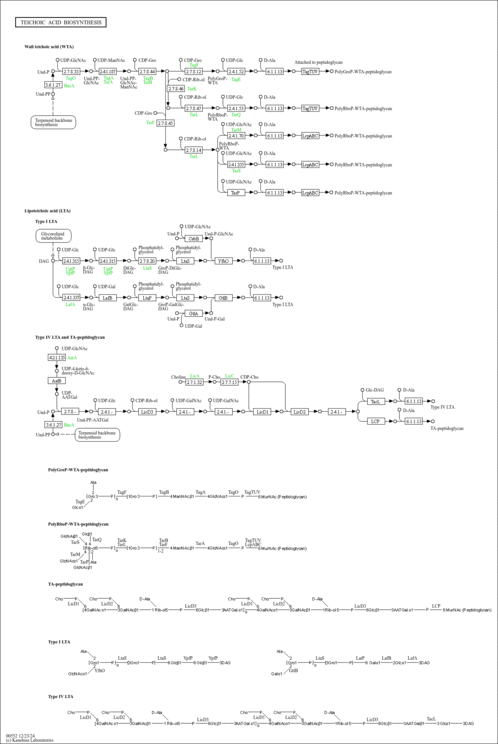
|
|---|
| Reaction |
| R01021 | ATP:choline phosphotransferase |
| R01890 | CTP:choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase |
| R05627 | undecaprenyl-diphosphate phosphohydrolase |
| R10266 | UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine hydro-lyase |
|
|---|
| Compound |
| C00043 | UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine |
| C04574 | di-trans,poly-cis-Undecaprenyl diphosphate |
| C04613 | UDP-2-acetamido-4-dehydro-2,6-dideoxyglucose |
| C17556 | di-trans,poly-cis-Undecaprenyl phosphate |
| G00177 | N-Acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-ditrans,octacis-undecaprenol |
| G10610 | UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine |
| G10611 | UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine |
| G11112 | UDP-N-acetyl-D-mannosamine |
| G13163 | beta-GlcNAc-P-undecaprenol |
| G13164 | N-Acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-ditrans,octacis-undecaprenol |
| G13165 | 4-O-[(2R)-1-Glycerophospho]-N-acetyl-beta-D-mannosaminyl-(1->4)-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosaminyl-diphospho-ditrans,octacis-undecaprenol |
| G13168 | Und-PP-GlcNAc-ManNAc-GroP-RboP |
| G13174 | alpha-O-GlcNAcylated WTA |
| G13176 | beta-O-GlcNAcylated WTA |
| G13184 | Polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid |
| G13190 | Polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Rismondo J, Gillis A, Grundling A |
|---|
| Title |
Modifications of cell wall polymers in Gram-positive bacteria by multi-component transmembrane glycosylation systems. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Guo Y, Pfahler NM, Volpel SL, Stehle T |
|---|
| Title |
Cell wall glycosylation in Staphylococcus aureus: targeting the tar glycosyltransferases. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Han X, Sun R, Sandalova T, Achour A. |
|---|
| Title |
Structural and functional studies of Spr1654: an essential aminotransferase in teichoic acid biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Rismondo J, Percy MG, Grundling A. |
|---|
| Title |
Discovery of genes required for lipoteichoic acid glycosylation predicts two distinct mechanisms for wall teichoic acid glycosylation. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Gisch N, Schwudke D, Thomsen S, Hess N, Hakenbeck R, Denapaite D. |
|---|
| Title |
Lipoteichoic acid of Streptococcus oralis Uo5: a novel biochemical structure comprising an unusual phosphorylcholine substitution pattern compared to Streptococcus pneumoniae. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Percy MG, Grundling A. |
|---|
| Title |
Lipoteichoic acid synthesis and function in gram-positive bacteria. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Brown S, Santa Maria JP Jr, Walker S. |
|---|
| Title |
Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Reichmann NT, Cassona CP, Grundling A. |
|---|
| Title |
Revised mechanism of D-alanine incorporation into cell wall polymers in Gram-positive bacteria. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Brown S, Xia G, Luhachack LG, Campbell J, Meredith TC, Chen C, Winstel V, Gekeler C, Irazoqui JE, Peschel A, Walker S |
|---|
| Title |
Methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus requires glycosylated wall teichoic acids. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Allison SE, D'Elia MA, Arar S, Monteiro MA, Brown ED |
|---|
| Title |
Studies of the genetics, function, and kinetic mechanism of TagE, the wall teichoic acid glycosyltransferase in Bacillus subtilis 168. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Reichmann NT, Grundling A. |
|---|
| Title |
Location, synthesis and function of glycolipids and polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid in Gram-positive bacteria of the phylum Firmicutes. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Brown S, Meredith T, Swoboda J, Walker S |
|---|
| Title |
Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis W23 make polyribitol wall teichoic acids using different enzymatic pathways. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Webb AJ, Karatsa-Dodgson M, Grundling A. |
|---|
| Title |
Two-enzyme systems for glycolipid and polyglycerolphosphate lipoteichoic acid synthesis in Listeria monocytogenes. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Sewell EW, Pereira MP, Brown ED |
|---|
| Title |
The wall teichoic acid polymerase TagF is non-processive in vitro and amenable to study using steady state kinetic analysis. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Meredith TC, Swoboda JG, Walker S. |
|---|
| Title |
Late-stage polyribitol phosphate wall teichoic acid biosynthesis in Staphylococcus aureus. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Brown S, Zhang YH, Walker S |
|---|
| Title |
A revised pathway proposed for Staphylococcus aureus wall teichoic acid biosynthesis based on in vitro reconstitution of the intracellular steps. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Zhang YH, Ginsberg C, Yuan Y, Walker S |
|---|
| Title |
Acceptor substrate selectivity and kinetic mechanism of Bacillus subtilis TagA. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Bhavsar AP, Truant R, Brown ED |
|---|
| Title |
The TagB protein in Bacillus subtilis 168 is an intracellular peripheral membrane protein that can incorporate glycerol phosphate onto a membrane-bound acceptor in vitro. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
| Reference |
|
|---|
| Authors |
Soldo B, Lazarevic V, Karamata D |
|---|
| Title |
tagO is involved in the synthesis of all anionic cell-wall polymers in Bacillus subtilis 168. |
|---|
| Journal |
|
|---|
Related
pathway |
| rn00900 | Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis |
|
|---|
| KO pathway |
|
|---|